Withdrawals from Xanax
Withdrawals from constant high doses of Xanax and even low dose Xanax withdrawal symptoms can lead to well-meaning patients, experimenters, or recreational users scurrying to rehab or looking for other ways to quit. Xanax withdrawal can be dangerous, so keep reading to be sure you know what are the side effects of Xanax and how to address them.
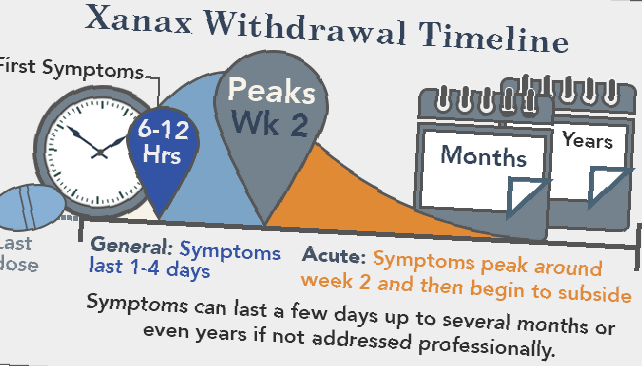
Figure 1.https://americanaddictioncenters.org/withdrawal-timelines-treatments/xanax
What is alprazolam and what is it used for?
Alprazolam is the medical name for possibly the most popular anti-anxiety drug, brand named Xanax. It falls into the class of short-acting benzodiazepine. These drugs act on the GABA A receptor, inhibiting neurons from firing and calming the nervous system. Xanax is a positive allosteric modulator of the GABA A receptor. GABA is the main inhibitory receptor in the human brain, while glutamate receptors are the main excitatory receptors. It works as an anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, anti-depressant, hypnotic, amnesic, and muscle relaxer. It has been shown to increase dopamine in the striatum to a greater extent than lorazepam, and this may be a mechanism of antidepressant action.
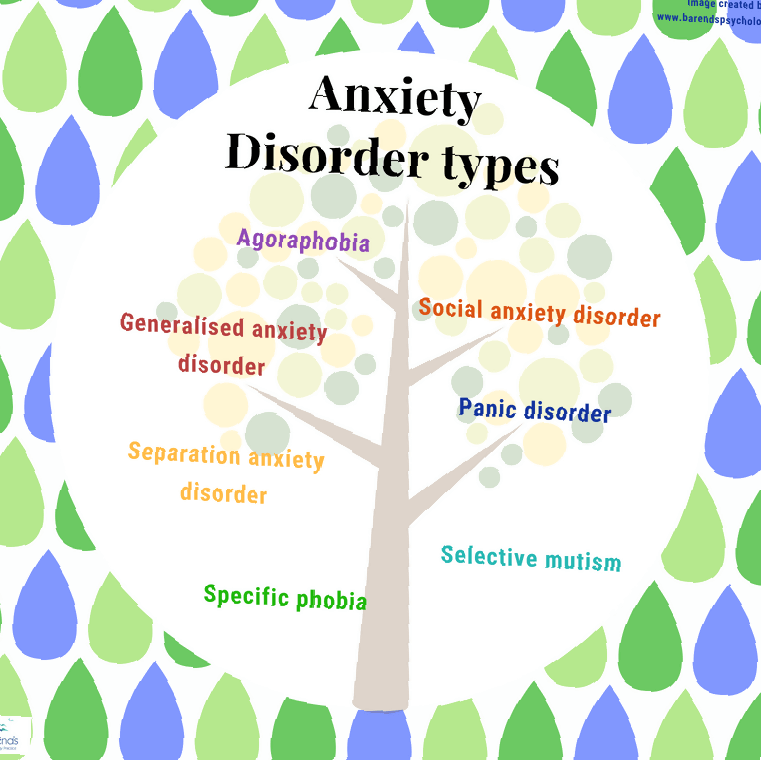
Xanax is used for the treatment of anxiety disorders such as Generalized Anxiety Disorder, which features free-floating anxiety not aimed at a specific phobia. It can also be used for intractable nausea caused by chemotherapy treatments for cancer, and for Panic Disorder, where subjects experience extreme panic symptoms such as a feeling of doom, shaking, and sweatiness. Although it is indicated for the short-term treatment of anxiety, patients routinely use it for long periods of time. Tolerance may set in and dose increases may be necessary.
Anxiety Disorders
Xanax is indicated for the treatment of anxiety disorders such as Generalized Anxiety Disorders and Social Anxiety Disorder. It is indicated for short term use, from 4 weeks to as long as 4 months. However, tolerance may set in and dose increases may be needed, especially if used for more than 4 months, which happens routinely. Because it is short-acting, Xanax may need to be dosed several times per day.
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is characterized by sudden bouts of extreme fear, panic, and a host of physical symptoms of anxiety-like breathlessness, shaking, and sweating. This state typically lasts a few minutes then passes. However, the sufferer can then gain a fear of having another panic attack and it can have a large adverse effect on important areas of life like work, school, and relationships.
Xanax can treat panic disorder. The preferred treatment for panic disorder is now SSRI’s, serotonin reuptake inhibitors, but when those are contraindicated, Xanax is a second-line treatment. It is indicated for use for up to 10 weeks. Long courses of treatment are discouraged against due to the development of tolerance and risk of addiction. Doctors have to assess the risk of addiction before treating a patient with panic disorder with Xanax. Past problems with pills or alcohol are a red flag that the patient could be at risk of becoming addicted to Xanax.
Xanax is approved by the FDA to treat Panic Disorder, and Panic Disorder with Agoraphobia (fear of leaving the house).
Xanax may be used off label for depression due to its unique antidepressant qualities.
Intractable nausea caused by chemotherapy
Xanax can be used to treat intractable nausea caused by chemotherapeutic medicines used to treat cancer. These medicines can cause nausea and vomiting which does not respond to OTC anti-emetics like meclizine. Xanax can be a life-saver for such patients and can allow them to gain the weight needed to recover from cancer.
FAQ about Xanax
Xanax is taken by mouth and readily absorbed with as much of 80 percent of the drug making it into the bloodstream. It goes into effect almost immediately, taking between 15 minutes and an hour to hit.
Xanax Xr is the extended-release form of Xanax. While immediate relief Xanax peaks in 2 hours and needs to be dosed several times per day, Xanax XR can maintain a steady level of Xanax in the bloodstream for 5 to 11 hours and be effective for that long. Immediately release Xanax may still be detectable in the bloodstream for 11 hours but levels are too low for it to continue being effective.
11.2 hours. While immediate release Xanax will take 11.2 hours for half the dose to be metabolized, it’s effectiveness maybe 4 hours or less.
A:
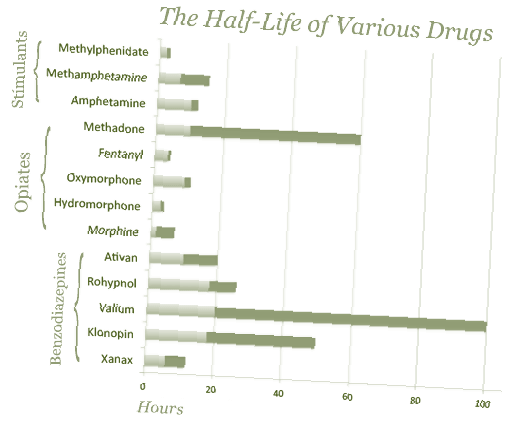
Figure 2.https://theoakstreatment.com/drug-addiction/long-drugs-stay-system/
The official word on Xanax is that is has a low potential for abuse if used as prescribed. Low dose Xanax is not addictive in and of itself. However, the anxiety which is being treated, as it returns upon cessation of Xanax use, can lead to patients staying on Xanax indefinitely. This can lead to dose escalation and eventual abuse and addiction.
Xanax can cause sedation, relaxation, and an alcohol-like buzz. When abused with alcohol, it can cause extreme sedation, lack of inhibitions, and euphoria. People abuse it sometimes during parties in order to make the effects of alcohol much stronger.
Xanax can acutely cause sedation, lack of awareness and care for your body and the environment, confusion, and forgetfulness. This is caused by excessive agonism of the GABA A receptor and this is one means by which Xanax can be harmful to the brain.
Another means of neurotoxicity is that chronic use of Xanax can cause downregulation of the GABA receptor, aka tolerance. Not only will it take more Xanax to relax, but it may also be harder to relax in general so anxiety levels may increase anytime the Xanax runs out or low. Finally, if one has to withdraw from Xanax, the rebound anxiety can raise glutamate levels severely and cause delirium tremens in the worst case, which is severe alcohol withdrawal, or in the more common cases, just panic attacks. The glutamate excess and excitotoxicity can cause damage to neurons, the same as happens in alcohol withdrawal.
Use of prescribed doses of alprazolam, aka Xanax, does not cause a high. However, excessive doses, especially combined with alcohol or opioids, will cause a high, or potentiate the alcohol or opioid high.
A:
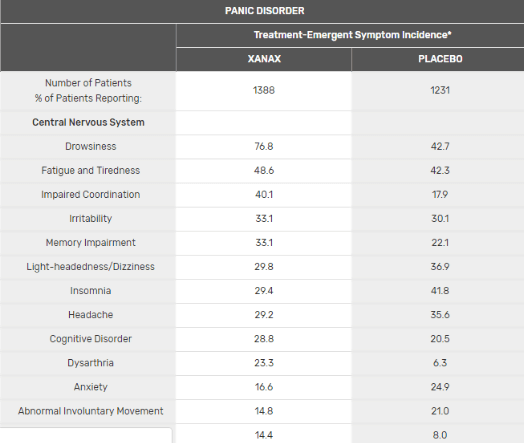
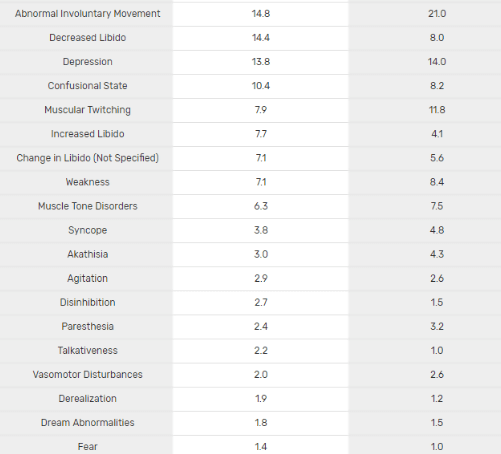
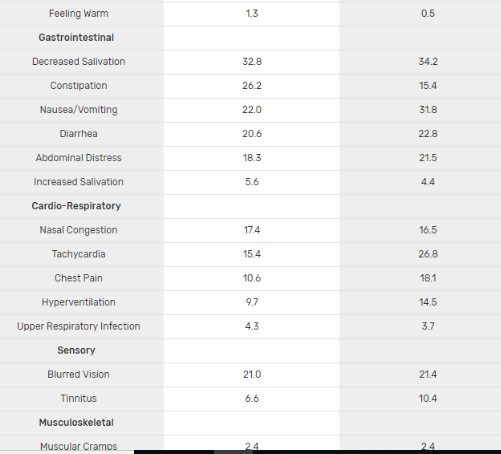
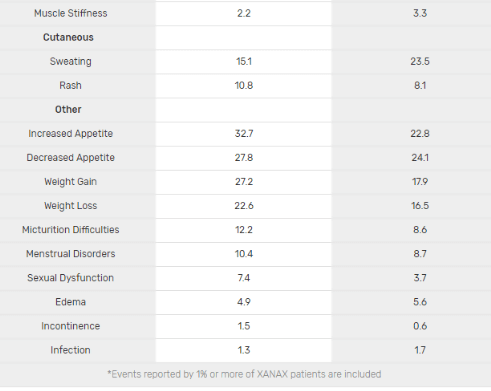
Xanax has several side effects typically associated with benzodiazepines. This includes drowsiness, depressed mood, fatigue, cottonmouth, and forgetfulness. When quitting Xanax or even reducing dosage, patients may experience rebound anxiety or even withdrawal symptoms which mimic a hyperadrenergic, anxious state. While officially marketed as having a low abuse potential, Xanax is frequently used to potentiate alcohol and opioids, leading to marked tolerance, physical dependence, and psychological addiction.
When the dosage of Xanax is decreased or discontinued, a withdrawal syndrome can ensue. Symptoms of excessive adrenaline and stimulation are present. This may include panic attacks, insomnia, shakiness, and sweating. The anxiety can be tremendous, depending on the dosage stopped. In the most extreme case, withdrawal can cause delirium tremens, a condition featuring intense anxiety, seizures, and hallucinations, associated mostly with withdrawal from large amounts of alcohol.
Signs & Symptoms of Xanax Withdrawal
Xanax binds to benzodiazepine sites of the GABA A receptors. Misuse will cause downregulation GABA signaling. This downregulation brings the brain back to homeostasis in the presence of the drug but causes tolerance to develop and overstimulation in the absence of the drug. When discontinuing use as prescribed or discontinuing after a period of misuse, the dose should be gradually reduced to minimize the effects of withdrawal. Some studies show that most users actually reduce their dosage to an ‘as needed’ pattern, rather than increasing the dose and becoming addicted. Those who are susceptible to addiction include those who have abused alcohol or benzodiazepines in the past, people with psychological conditions, and recreational abusers of the medication.
It is a controversial claim (which research suggests is false) that regular use of Xanax for anxiety control leads to addiction. However, abuse is common as Xanax is a short-acting benzodiazepine, has immediate effects, increases euphoria when used with alcohol and opioids, and brings down users of cocaine and methamphetamine who have become overstimulated or paranoid. It is popular in the cabinet of abusers of various drugs. Abusers of Xanax may become physically dependent on Xanax and other drugs like alcohol or Oxycontin in combination. Xanax is sometimes called 4 bar or bars because of how the 2 mg form is a bar divided into 4 squares so that breaking a piece off is easy to do. It is also called Zanies. It is commonly assumed the rapper Lil Zan derives his rap name from his admitted Xanax addiction.
| Xanax Withdrawal Symptoms |
|
Factors Affecting Withdrawal
The biggest factor affecting Xanax withdrawal is the dosage. Using 4 mg per day or more puts the user at a greater chance of experiencing withdrawal symptoms. The higher the dosage and the greater the frequency of dosage, the more severe the withdrawal.
| Factors affecting withdrawal symptoms |
|
Xanax Withdrawal Timeline

As you can see, Xanax withdrawal can be a drawn-out affair. Symptoms can peak around the second week, then begin to decrease.
In the worst-case scenario, when Xanax is abused with alcohol and both are stopped suddenly, there can be withdrawal seizures and delirium tremens. Abuse of high doses of Xanax even without alcohol can cause delirium tremens. The DTs as it is called has a high fatality rate. Paradoxically, benzodiazepines of the long-acting variety are also used to treat DTs from alcohol or benzodiazepine withdrawal. Untreated cases can result in death.
Delirium tremens from alcohol and Xanax withdrawal
There is no risk of delirium tremens with use of Xanax as prescribed. Only abuses of high doses over a long period of time produces a risk of delirium tremens. Seizures can also occur in withdrawal from high doses.
Use of alprazolam during pregnancy of nursing can cause fetal abnormalities and can cross into breastmilk and cause the baby to lose weight and become sedated. Use during pregnancy and nursing is discouraged.
Interactions
Xanax can potentiate alcohol and opioids, which can lead to blackouts, nodding, and respiratory depression which can be fatal when high doses of these drugs are used.
CYP3A4 inhibitors like cimetidine (stomach acid reducer) and ketoconazole (anti-fungal) can decrease the clearance of alprazolam and cause it to accumulate and produce side effects.
Combining Xanax with alcohol can cause severe intoxication and sedation. Combining Xanax with kava can cause a comatose-like state.
| Overdose |
|
Xanax Withdrawal Treatment Options
Xanax is a Schedule IV Controlled Substance. Schedule IV means that it has accepted medical uses, low abuse potential, and produces mild physical dependence.
Xanax is the most frequently abused benzodiazepine; however, most users do not abuse their prescription. When one needs to withdraw from Xanax, the first thing one needs to know is if possible, it must be done gradually.
Gradual Dose reduction
The method of dose reduction to get off of Xanax is called tapering. This should be done under medical supervision at a hospital or rehab. Your average rehab center will be able to handle this. They should know all the substances you are withdrawing from and all the substances you use. Be sure they have a doctor running the center and they know that Xanax withdrawal is similar to alcohol withdrawal. There is a risk of seizures and delirium tremens if you stop very high doses of cold turkey.
To taper off Xanax a doctor might reduce the dosage 5% to 10% every week, or you can try an aggressive approach of 25% per week. For example:
Week 1: Same dose, say you’re using 4 mg per day.
Week 2: 25 percent, reduction to 3 mg. You reduce by one little square of your Xanax bar.
Week 3: 25 percent reduction (.25 * 3 mg = .75 3mg – .75mg = total daily dosage 2.25 mg or 2 ¼ squares)
Week 4: Total reduction by one half.
Week 5-8: Maintain dose if at a therapeutic dose.
Week 9 and Beyond: 25 percent reduction per week until abstinence or you reach the desired dosage.
A doctor might instead switch you to a longer-acting benzodiazepine like diazepam. The dosage will be taken less frequently and the detox schedule will be different. If your cases respond to longer-acting benzo, this is the better option. However, sometimes the only thing to get you off is tapering off what got you addicted in the first place.
Conclusion
Xanax is a very useful medication for anxiety and depression. It is short-acting and has antidepressant properties. A minority of people will become addicted to it or use it for the purpose of potentiating other drugs like alcohol or opioids. If you get addicted, go to treatment in order to taper off under medical supervision. Quitting high doses of cold turkey can be uncomfortable and in extreme cases combined with alcohol withdrawal, can be fatal.





