Gabapentin long term side effects
How long does gabapentin withdrawal last?
This exchange highlights a little known fact about gabapentin, it can have a withdrawal syndrome. Gabapentin is often prescribed as a less addicting way to treat neuropathic and chronic pain. However, some people are under the impression that there is no addiction and no withdrawal. Our sources in social media beg to differ.
Symptoms


This Reddit user described some of the symptoms he experienced withdrawing from gabapentin and a few other CNS depressants. Many of these symptoms are applicable to gabapentin withdrawal alone. Many people described depression, shaking, vibrating, pain, and fatigue.

This describes an amotivational syndrome experienced by those who withdraw. They lack motivation, they can barely move. They are sensitive to the slightest amount of stress. They feel heavy, tired, and their physical strength is drained.
Psychiatrist fail


This Reddit user says her psychiatrist told her gabapentin causes no withdrawals. We consider that a fail. Regardless of what the company line is on the substance, long-term use of high doses when stopped cold turkey is without a doubt associated with a withdrawal syndrome in some if not all users.
As you can see, there is a large amount of misinformation out there about gabapentin, among users and doctors alike. Let’s see if we can’t clear up some confusion.
What Is Gabapentin (Neurontin)?
Gabapentin is a drug of the anticonvulsant class. It goes by many names, including Neurontin and Gralise. Here are some of the conditions is it used for:
- Neuropathic pain (shingles, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue, multiple sclerosis)
- Restless leg syndrome
- Partial seizures
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Postherpetic neuralgia
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder and other anxiety disorders
- Bipolar disorder
- Insomnia
- Alcohol withdrawal symptoms
- Opioid withdrawal symptoms
Many of these uses are off-label. Gabapentin may be combined with other pain medication such as oxycodone to enhance the pain-relieving effect.
Side Effects
Gabapentin can have the following side effects
| Gabapentin Side effects |
|
Gabapentin appears to have fewer side effects than opioid pain medications. Since it is not a scheduled substance in most states, doctors are more comfortable prescribing it than other pain medications like Percocet and Roxicontin. However, doctors may tend to overestimate the lack of side effects and underestimate the potential for abuse, dependence, and withdrawal. Recently, gabapentin is being found to be a factor in opioid abuse as many of those with addiction, unable to get benzodiazepines, will combine opioids with gabapentin to potentiate the high.
Interactions with other drugs
Gabapentin is known to potentiate opioids like oxycodone, hydrocodone, and morphine. This can raise the risk of getting high, nodding, and respiratory depression.
Using the Maalox antacid can reduce gabapentin uptake. Keep the medications apart by at least two hours.
Gabapentin can have a synergistic effect with alcohol.
Gabapentin overdose
It is possible to overdose on gabapentin even though it’s just an analog of GABA, an endogenous neurotransmitter.
| Overdose symptoms can include |
|
Pharmacology
Gabapentin was created to resemble the neurotransmitter GABA or gamma-aminobutyric acid. This is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system, gut, and immune system. The GABA receptor is the main target of alcohol, kavalactones, and substances like GHB. It has many subtypes and binding sites. However, upon examination, they did not find that gabapentin had an affinity to the receptor at any intensity that would explain the effects of gabapentin. They later discovered that gabapentin appears to bind to the α2δ subunit site of certain voltage-dependent calcium channels where it inhibits calcium influx. This is expected to also have an inhibitory effect on the central nervous system by stopping neurons from firing.
How long does it take for gabapentin to work for anxiety?
Gabapentin is used off label for anxiety disorders. It works for some people, for others, it does not work, and for still others, it makes things worse. If it’s going to work, some improvement should be noticed in one week. Full effects may take a month.
Gabapentin for nerve pain how long does it take to work?
Gabapentin is used for nerve pain such as in shingles. It is sometimes a great boon to those who prefer not to use opioids for their pain. Improvement should be noted as soon as the effective dose is reached. Since dosing must start low to assess tolerance, it can take several months to reach the effective dose, or it can take mere weeks. Once the effective dose is reached, marked improvement should be noticed.
Gabapentin for opioid withdrawal
Doctors looking for less addictive medications to aid in opioid withdrawal have looked to gabapentin to reduce the pain and fatigue from opioid withdrawal. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology in 2011 found that a dose of 1600 mg per day of gabapentin had a significant positive effect on withdrawal symptoms of those undergoing methadone-assisted detoxification (Salehi, Kheirabadi, and Maracy). Doctors treating opioid withdrawal have long noticed these positive effects and have combined gabapentin with other drugs like clonidine and hydroxyzine to aid in helping people withdrawing from opioids. In the study, 1600 mg per day was significantly superior to 900 mg per day. Therefore, dosage matters, with the higher dosage showing greater efficacy in those who tolerate it.
Gabapentin recreational dose: how many mg of gabapentin to get high?
Post-marketing reports have shown that those previously addicted to other substances are at risk of abusing prescriptions of gabapentin.
The following report from Erowid describes a typical attempt to use gabapentin recreationally.
Gabapentin high experience


It typically takes about 2 hours for the dose to kick in. Abusers may take anywhere from 400 to 1200 mg at a time. Users generally get very chatty and loose. Some people may get drowsy but more often people describe feeling like they have more energy and fewer inhibitions. Users may have a flight of thoughts. They may boost the effect by having coffee. There is a marked lightness from the pain relief and a rise in motivation to get work done. It works mainly as a disinhibitor. Most people do not report sedation unless very high doses are used. Overdoses can result in seizures. If combined with opioids or alcohol, respiratory depression and death are possible.
Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms
Gabapentin withdrawal: signs, timeline, symptoms, coping, and recovery
Like the user above, abusers of gabapentin may take doses of 3000 mg or more every day. Since gabapentin is a GABA analog, one would think this would not be terribly dangerous. It’s not as dangerous as abusing oxycodone but it can cause some effects reminiscent of alcohol or benzodiazepine abuse. Since it does not directly affect GABA or opioid receptors, it does not cause opioid withdrawal or delirium tremens. It does have a unique withdrawal syndrome of its own.
| Gabapentin Withdrawal Symptoms |
|
These appear 7 hours to 24 hours after the last dose of gabapentin. They can cause marked panic. Sometimes the only remedy is to reintroduce gabapentin then wean off.
What Causes Gabapentin Withdrawal?
Gabapentin withdrawal appears to be similar to withdrawal from benzodiazepines and alcohol withdrawal, even though as far as we know, it does not attach to GABA receptors. It may yet affect the same receptors indirectly. Due to this similarity, withdrawal from gabapentin needs to be done by tapering over weeks or months, not mere days. Because the mechanism of action is not well-understood, doctors are likely to start a patient back on gabapentin until symptoms resolve, then to initiate a very slow taper. They may reduce the dose by 10 percent every 1 to 4 weeks until the patient is no longer dependent. As you can see, this can take a very long time. Dangerously high doses are not likely to be maintained by a doctor, so you should expect the doctor will knock you down to 2400 mg immediately, then taper from there, unless that causes severe medical complications.
How Long Does Withdrawal From Gabapentin Last?
It is not well-known medically how long gabapentin withdrawal lasts. However, it follows a pattern similar to benzodiazepine withdrawal.
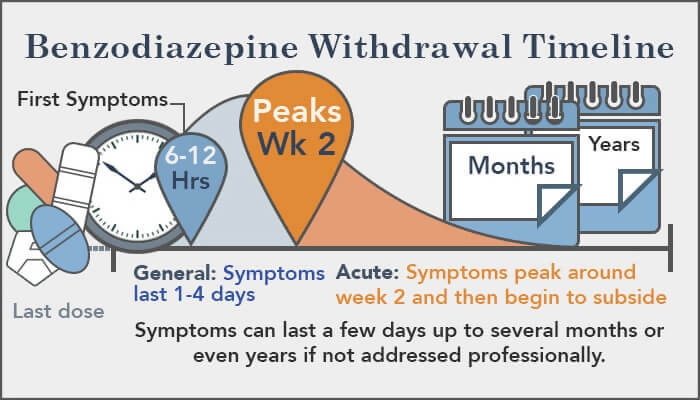
Figure 1.https://americanaddictioncenters.org/benzodiazepine/length-of-withdrawal
It should be noted, many people who use doses of 2400 mg and under, do not have significant withdrawal upon discontinuation. They may have a little anxiety and shaking for about 3 days than return to baseline. Those who abuse higher doses for longer periods can have a more serious withdrawal. We estimate that the peak of gabapentin withdrawal probably comes a bit sooner than that of benzodiazepines. In all, the withdrawal will be slightly milder than withdrawal from benzodiazepines or alcohol.
Is Gabapentin a Commonly Abused Drug?
Gabapentin is not commonly abused alone. Abusers whose drug of choice is opioids or alcohol may combine their drug with gabapentin, especially if they are unable to get benzodiazepines like Xanax or pregabalin, another GABA analog more powerful than gabapentin. Gabapentin is becoming more widely recognized as a drug which may accompany abuse or heroin, fentanyl, and other opioids. Kentucky, West Virginia, and Ohio have made gabapentin a controlled substance by state law due to a number of opioid overdose deaths in which gabapentin was shown to be a factor.
Effects of Gabapentin abuse
Gabapentin abuse can cause problems in the addict’s personal life. The abuser may become forgetful or agitated easily and this can affect personal relationships. Loss of inhibition can cause the person to behave out of character and say or do things they regret. They can lose jobs. They can lose money due to the need to buy gabapentin off the street. Rarely is gabapentin alone the culprit, but rather using gabapentin to potentiate opioids or alcohol interferes in the addict’s ability to function.
There is some evidence that long-term use of gabapentin can cause damage to the brain, immune system, or kidneys. A study at Stanford discovered that gabapentin stops the formation of new synapses in the brain. This can greatly impair learning. This is proposed as the mechanism of the drug’s anti-seizure activity. Due to the lack of connectivity in the brain, the seizure networks are disrupted. However, new learning may also be disrupted. Adult brains form few new synapses but taking gabapentin during pregnancy could put the newborn at risk for mental disorders or could require drug withdrawal treatment after birth.
Conclusion
Gabapentin can be a life-saver for those with seizure disorders or neuropathic pain. However, it can be addictive and can have a little recognized withdrawal syndrome. When going off of gabapentin, it is imperative that a doctor tapers the dose over a long period of time.
General Medical Disclaimer
Leaf Expert is not dispensing medical advice. If you have a problem with addiction, contact your doctor or an addiction treatment center.
FDA Disclaimer
Gabapentin is not a controlled substance federally. It is controlled in Kentucky, West Virginia, and Ohio. If you have a problem with addiction, seek professional help. Gabapentin is regulated by the FDA as a prescription drug.
Bibliography
Salehi, Mehrdad, et al. “Importance of Gabapentin Dose in Treatment of Opioid Withdrawal.” Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 31.5 (2011): 593-596. 15 7 2019. https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21869694.
- 1 How long does gabapentin withdrawal last?
- 2 What Is Gabapentin (Neurontin)?
- 3 Side Effects
- 4 Interactions with other drugs
- 5 Gabapentin overdose
- 6 Pharmacology
- 7 How long does it take for gabapentin to work for anxiety?
- 8 Gabapentin for opioid withdrawal
- 9 Gabapentin recreational dose: how many mg of gabapentin to get high?
- 10 Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms
- 11 What Causes Gabapentin Withdrawal?
- 12 Is Gabapentin a Commonly Abused Drug?
- 13 Effects of Gabapentin abuse
- 14 Conclusion
- 15 General Medical Disclaimer



