Active Ingredients in Marijuana
What are marijuana and the main elements of it?
Derived from dried flowering leaves, tops, seeds, and stems of a Cannabis sativa (hemp) plant is known as Marijuana. The primary active ingredient in marijuana is Cannabinoids. It is responsible for the medicinal and psychoactive effects (high) and is made of unique chemical structures. In recent years, the consumption of Marijuana in the United States especially for medicinal purposes has been on the rise due to various states legalizing its usage.
Chemicals in Marijuana
Are you wondering how many chemicals in weed? As many as 86 cannabinoids have been identified in nature and a few more have been synthesized chemically.
Chemical Formula for Marijuana
- Molecular formula: C21H30O2
- Molecular weight: 314.4 g/mol
Chemical Formula of THC
Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol or Δ9-THC also known as dronabinol (International Non-Proprietary Name) is the primary principle of marijuana products. It contains an unsaturated bond between the cyclohexene ring situated in between C-9 and C-10 among the common dibenzopyran ring numbering system. Although 4 stereoisomers are there in THC, it is only (-)-trans isomer that occurs naturally. (−)-(6aR,10aR)-6,6,9-trimethyl-3-pentyl- 6a,7,8,10a-tetrahydro-6H-benzo[c]chromen-1-ol is the full systematic name of this particular THC isomer. Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol-2-oic acid & Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-4-oic acid (THCA) is also a part of the cannabis plant.
The known substances from the cannabinoids list are:
- Cannabinoids (CBD)
- Cannabinol (CBN)
- Cannabavarin (THCV)
- Cannabigerol (CBG)
- Cannabichromene (CBC)
- Delta-8-THC
- Cannabicyclol (CBL)
- Cannabitriol (CBT)
- Cannabielsoin
- Cannabigerolic acid (CBGA)
- Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA)
- Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA)
- Cannabichromenenic acid (CBCA)
- Cannabigerovarinic acid (CBGVA)
- Tetrahydrocanabivarinic acid (THCVA)
- Cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA)
- Cannabichromevarinic acid (CBCVA)
Cannabinoids; Terpenes; Other Ingredients Tested
CBDA and THCA are abundantly available cannabinoid in the strains. The major cannabinoid acids are THCA, CBGA, CBCA, and CBDA. CBGA is used by enzymes of the plants to make the other three cannabinoids. Similarly, there is the same number of corresponding “V” compounds that have shorter chemical structures namely THCVA, CBGVA, CBCVA, and CBDVA. Unlike THC, Cannabinoid acids do not produce intoxicating effects. However, each of them has interesting properties of their own. Several cannabinoid acids are instilled with insecticidal and antibiotic properties.
The same glands producing cannabinoids like CBD and THC produces terpenes. They are aromatic oils that add distinctive flavors such as berry, pine, mint, and citrus to the cannabis varieties. Terpenes primarily differentiate the effects of cannabis strains. While some promote stress-relief and relaxation, others promote acuity and focus. The development of Terpenes started for adaptive reasons for repelling predators and luring pollinators. The weather, climate, maturation, age, soil, time and fertilizers play a critical role in the development of terpenes. In a cannabis plant, each strain has a unique terpene type and composition. There are over 100 different types where each descendant has a distinct smell of its own. Cheese strain has a cheese-like strain and Blueberry offspring smell like berries.
Extraction of cannabis also produces materials for use in edibles, oils, and products that utilize solvents like propane, butane, acetone, or isopropanol. Most of them are harmful which is the reason why they need to be absent from the final product. The industry today is working to adopt supercritical ethanol, carbon dioxide, and water as extraction processes.
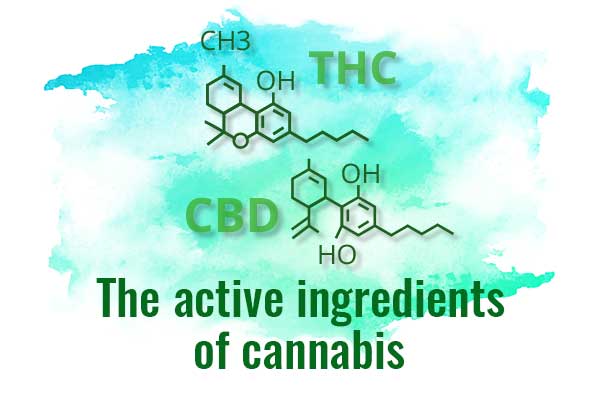
Medical cannabis active ingredients: THC & CBD
What is CBD? Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the 120 active substances found in marijuana. It is believed to be highly beneficial to relieve pain, nausea, treatment of chronic conditions, and inflammation. It is an essential element of medical marijuana and is directly derived from a hemp plant. Despite being a component of marijuana, it doesn’t cause high on its own. As per a report released by the World Health Organization, CBD has no side-effects or abuse on an individual or create a dependence potential. As of date, there is no evidence that points towards any health-related problems due to the use of pure CBD.
Delta-g-tetrahydrocannabinol or THC is the major psychoactive ingredient in marijuana. THC acts on specific brain receptors and may lead to depression, suicidal thinking, disruption in learning abilities, memory issues, and mood swings.
The psychoactive nature of delta-0-THC in marijuana is used for measuring the herb’s potency. Typically THC occurs in concentrations of about 0.5% in inactive hemp, 2-3% in marijuana leaf and 4-20% in higher-grade marijuana. The concentration of the plant is 10-20% more in case of seedless buds called sinsemilla. Higher concentrations are also found in extracts, hashish, and tonics.
The THC varies between 2.5 to 20 milligrams in Oral doses used for therapeutic uses. A 1 gram single joint comprises of 2.5% leaf or a 0.5 grams joint made of 5% higher grade leaf contains 25 milligrams of THC. Half of the total composition gets destroyed during side-stream smoke or combustion. On average, about 15-50% of the total THC from this marijuana joint reaches the bloodstream. Hence, the total inhaled dosage while smoking is close to 3-12 milligrams.