How Can You Use CBD Oil for Anxiety?
How much CBD oil to take for anxiety?
Instructions: We chose a 500 mg Crystalline tincture in MCT Oil to demonstrate how to take the CBD. You can also use a CBD hemp oil dosage for anxiety, as some people prefer hemp oil’s entourage effect due to the presence of other cannabinoids, terpenes, and the hemp oil itself. A full dropper of the product above is 16.66 mg of CBD oil mg dosage for anxiety. Start with one full dropper. Some recommendations suggest waiting 2 weeks before you increase the dose by another dropper at a different time of the day. However, one can experiment with increasing the dose sooner but do so gradually. Allow a few days to determine the effectiveness of initial doses. Choose a brand that gives clear content information and instructions such as the one above.
Labs like the one below will test your CBD oil dose for anxiety and tell you how much actual CBD is contained in it. They also publish results online for their own Cannabidiol product, so you can see upfront the product you purchase has the correct CBD levels.
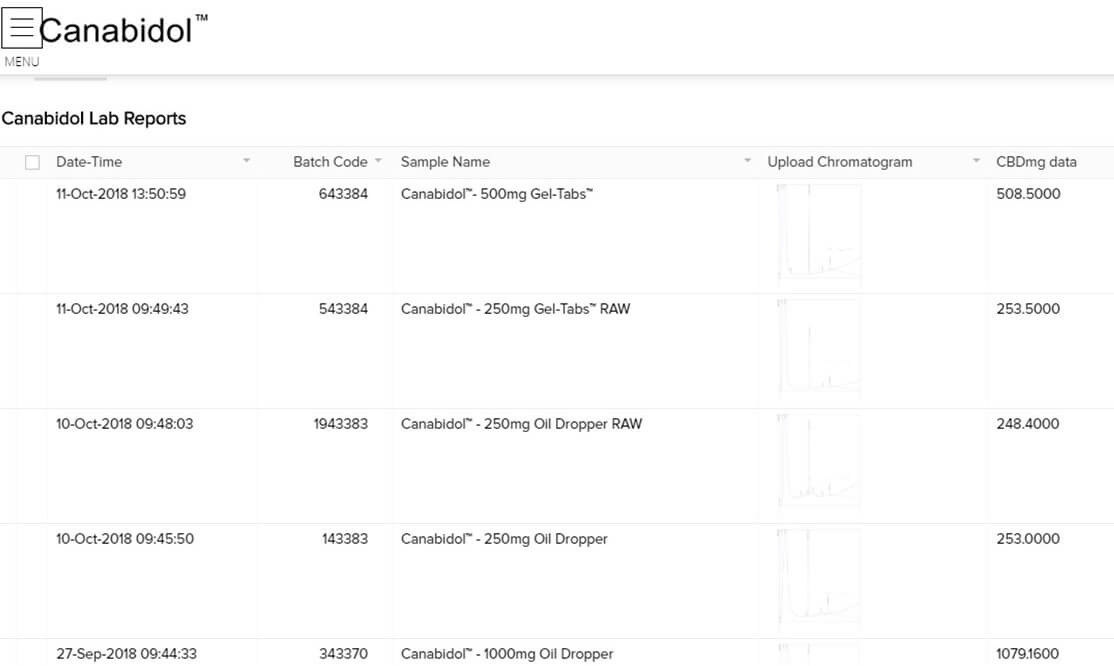
Figure 2.You can see from this chart, each of the products shown has the indicated level of CBD. However, it appears that this company is testing its own product, whereas we recommend you get a product that uses a third-party testing facility.
The best way you can use CBD oil for anxiety
Our choice: Sublingual
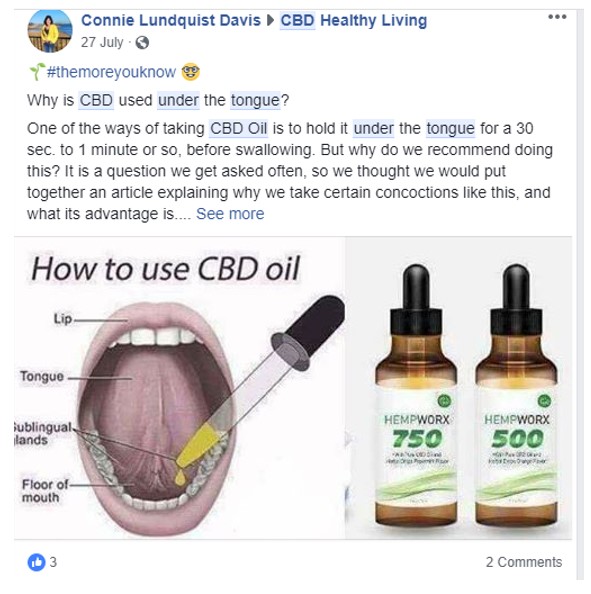

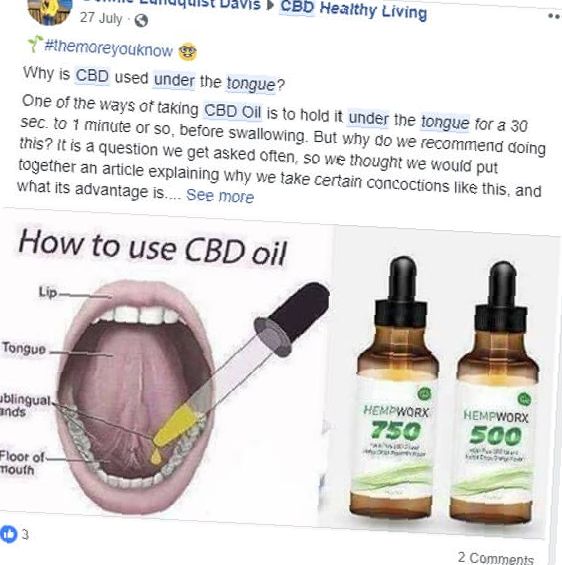

Figure 1. This Facebook user was nice enough to provide fairly consensus and accurate instructions for how you can use CBD oil under your tongue for anxiety.




It might be possible to contact a lab and ask the identity of these products which have proven to have the correct CBD levels. Remember up to 70% of products will not have the indicated levels of CBD.
How to Choose a CBD Oil for Anxiety
Once you choose a product, you can determine how many mg of CBD oil for anxiety is contained in your product and how much is in a dropperful. In most formulas, one dropper will be a starting dose, but always check the instructions on your particular product as they can have different concentrations and dosages of CBD. A study in Jama (2017) showed nearly 70 percent of CBD oil products sold online are mislabeled and therefore not containing the stated levels of CBD or THC (Bonn-Miller, et al., 2017). How do we go about finding the right product? One sure-fire way is to request a lab analysis from the company or from an independent lab, though the latter may be expensive. Some companies will send a lab analysis with your order, so you might favor those companies.
Preparation:
- Choose American vendors or vendors you have researched and trust.
- How is it made? Go to the website and to customer service and ask how the CBD oil is made. Favor supercritical CO2 extraction and alcohol extraction.
- Get the lab results and confirm the CBD oil is not psychoactive and not likely illegal because it has less than 0.3 percent THC.
- Use ‘entourage’ effect products that contain the whole plant, high CBD, and low or no THC. They will be labeled ‘whole plant’ or ‘full spectrum’. Isolates and crystalline products are for when you or your doctor have a specific need to avoid other ingredients and deliver a superior dose of CBD.
- 3rd party lab results. This is the most important consideration. Make sure they have an unaffiliated lab test their product and provide the results to them and you.
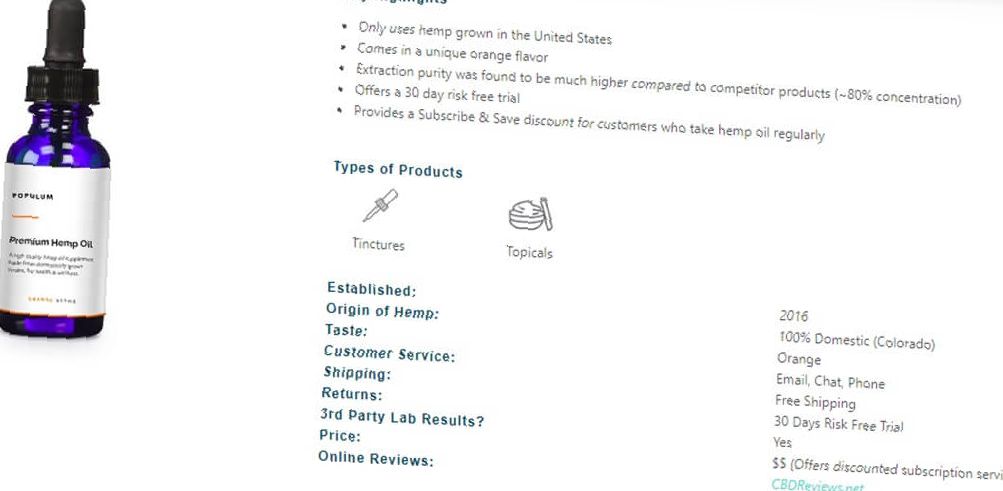
Below is an example of a product called Populum which passes each of the above requirements and can produce 3rd party test results.
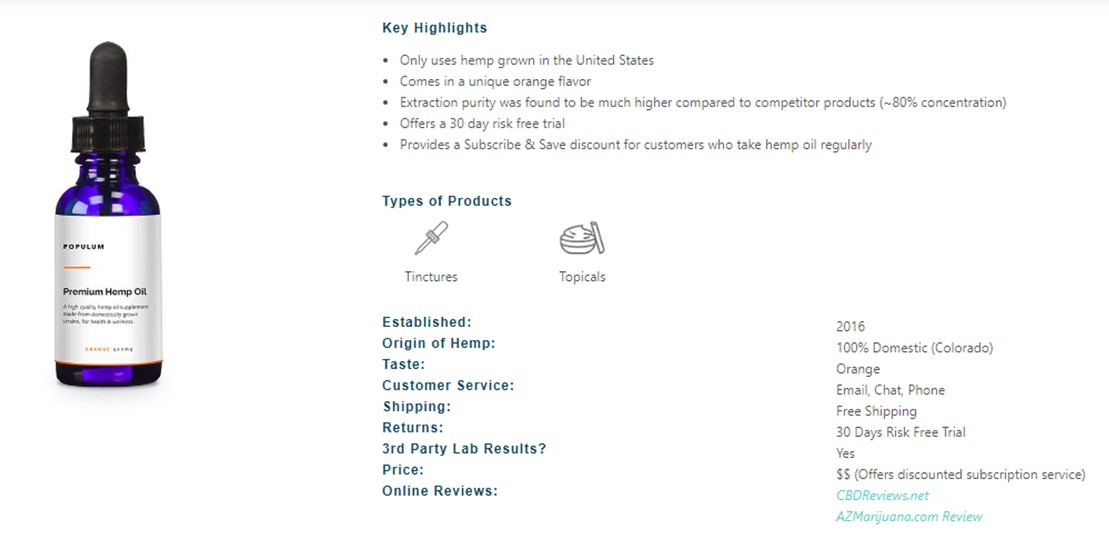


How does CBD oil work for Anxiety?
CBD oil has many different mechanisms of action. The chart below shows only the extensive effects of CBD on the nervous system. CBD oil may contain other therapeutic cannabinoids and terpenes in addition to the CBD component. It appears that CBD modulates serotonin 5ht1a receptors, cannabinoid receptors, and even affects opioid receptors. These receptors are known to be involved in pain and anxiety. The precise mechanisms by which CBD reduces anxiety do not fully know, though further research is pending.
These mechanisms of action reduce anxiety, inflammation, pain, and interferes with the persistence of pain and fear memories.
Mechanisms of action of CBD
- CB1 receptor ligand (indirect antagonist)
- CB2 receptor ligand (indirect antagonist)
- Increases CB1 receptor density
- GPR3 receptor (inverse agonist)
- GPR6 receptor (inverse agonist)
- GPR12 receptor (inverse agonist)
- GPR55 receptor (antagonist)
- Serotonin 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist
- An allosteric modulator of mu and sigma opioid receptors
- Glitazone receptor agonist
- Inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase, increasing levels of endogenous cannabinoids
Facts about anxiety, conventional treatment, and how CBD is better
Pros and cons CBD VS Conventional Treatment for Anxiety
| Pros |
|
| Cons |
|
Research on CBD for Anxiety
One of the first indications that CBD may be effective for anxiety as observed in a 1982 study in Psychopharmacology. This study demonstrated that cannabidiol and reduce the anxiety caused by THC (Zuardi, Shirakawa, Finkelfarb, & Karniol, 1982).
A 2011 study in Neuropsychopharmacology found that cannabidiol reduced anxiety caused by public speaking, which is consistently rated as the top anxiety-producing situation (Bergamaschi, et al., 2011).
A review of studies on the actions of CBD on anxiety published in the Frontiers in Pharmacology in 2016 found that cannabidiol may affect anxiety levels in 3 ways: (1) decreasing anxiety immediately, (2) disturbing the emotional memory of the fear so that it does not express when the memory is retrieved, (3) enhancing the effects of exposure therapy, which is the gradual introduction of contact with the feared object (Jurkus, et al., 2016).
A study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology in 2018 used CBD to test symptoms of paranoia in a high-trait paranoia group in a computer-simulated environment. This study found no effects of CBD oil on paranoia. However, paranoia is not synonymous with anxiety. Also, the study design is full of confounders such as using a sample of non-diagnosed persons and using a virtual reality environment (Hundal, et al., 2018). Also, the study was largely aimed at demonstrating the effectiveness of virtual simulation in producing an anxiety effect and is an effective study model for anxiety.
A study published in the British Journal of Pharmacology in 2017. Found that cannabidiol modulation of serotonin 5ht1a receptors caused effects on cannabinoid receptors which reduced anxiety acutely as well as decreased the reconsolidation of anxiety-related memories and memories about substance abuse, therefore, reducing fear-related triggers for substance abuse (Lee, Bertoglio, Guimarães, & Stevenson, 2017).
A study published in The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology in 2010 observed a disruption of prefrontal-subcortical brain regions as part of the mechanism of CBD’s anxiolytic effect. The disruption of these regions inhibited the fear response to angry faces, a common means of inducing immediate fear reactions under test conditions (Fusar-Poli, et al., 2010).
Reviews: Wisdom of Social Media
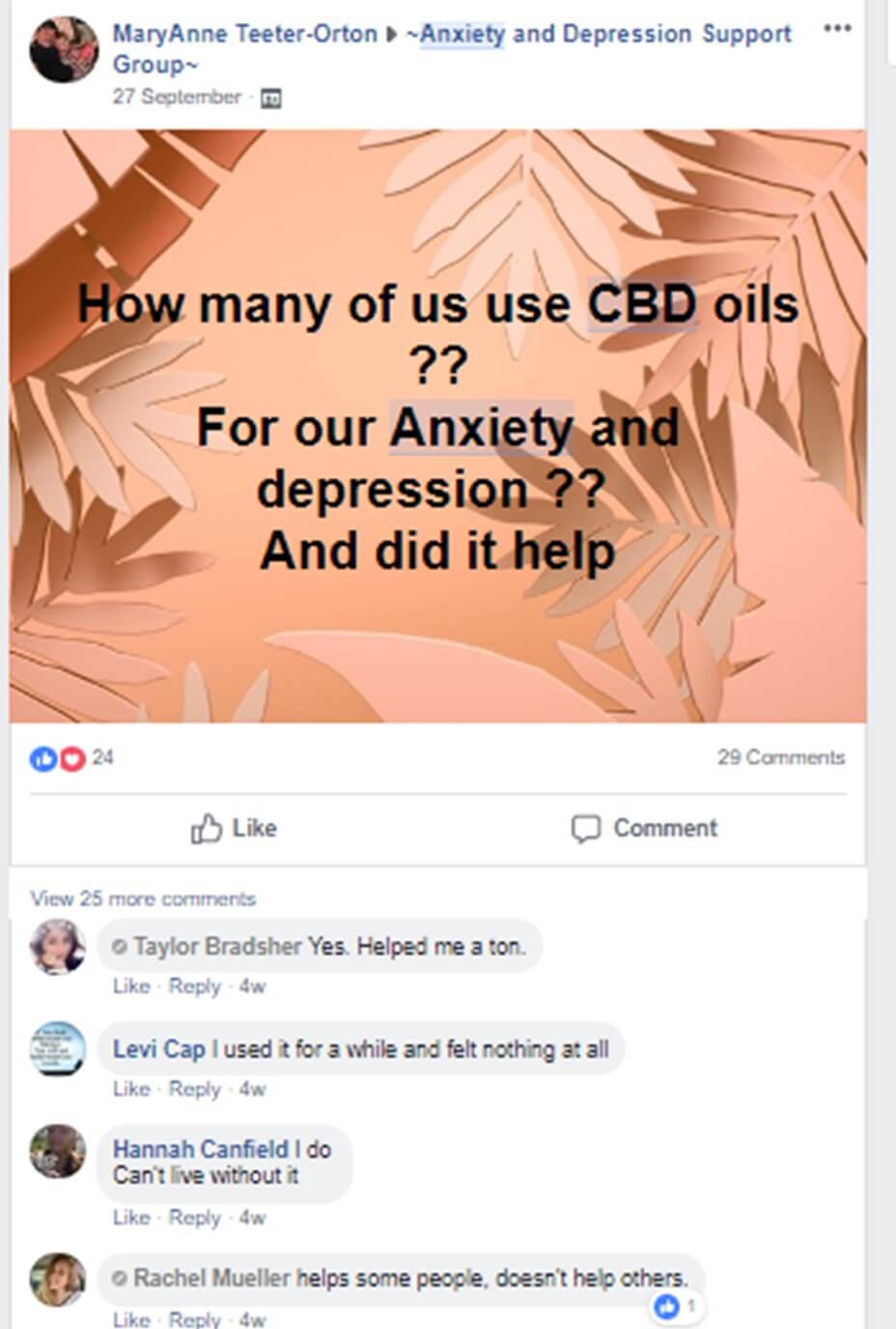


Comment: Our friend Rachel has got it fairly right. It helps some, doesn’t help others, but surely worth a try.
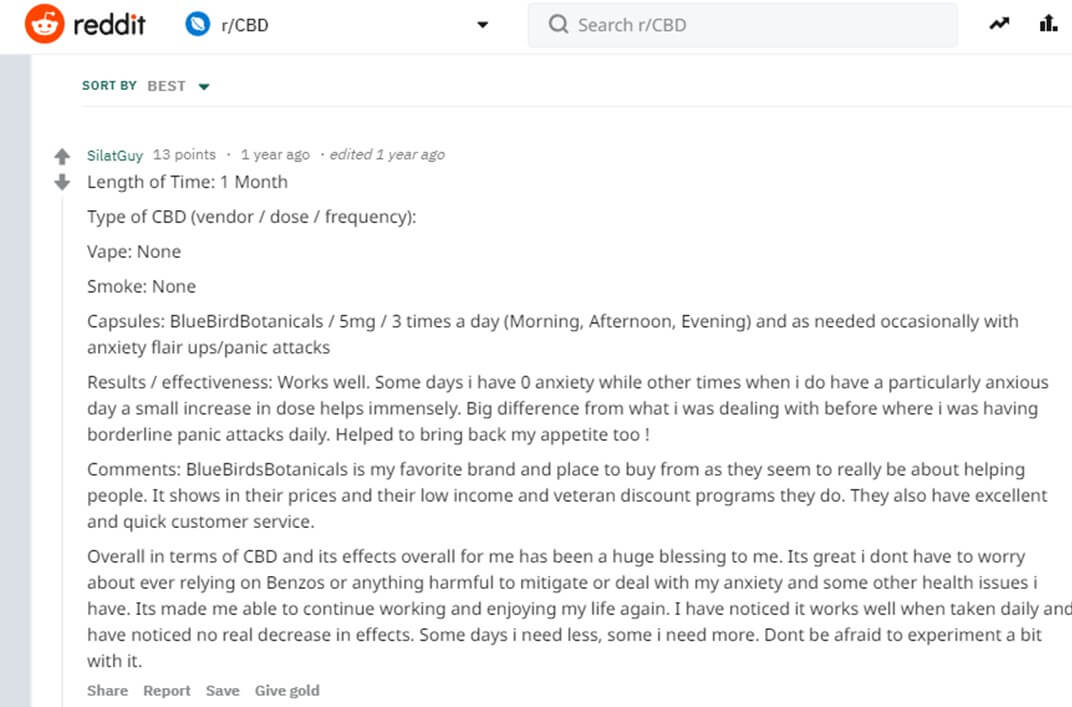


Comment: This Reddit user surely has a very informed opinion and claims that CBD sometimes gives him days with no anxiety symptoms.
About Anxiety
Anxiety is a condition where fear becomes chronic and recurrent to the point that it is interfering significantly with one’s ability to have a quality life. Anxiety is a natural response to many challenges. It is only pathological when it appears too frequently, is of excessive strength (heart palpitations, excessive sweating, hyperventilation), or interferes with normal life activities (school, work, sleep, eating, etc.).
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders lists several Anxiety Disorders:
- Agoraphobia
Fear of leaving the house or the company of family members or other trusted individuals.
- Generalized anxiety disorder
Free-floating anxiety which does not have one specific object.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
The anxiety has driven the development of obsessions which provoke anxiety which is mildly relieved by performing superstitious rituals.
- Panic disorder
Characterized by a sudden feeling of dread or terror, lasting several minutes, and producing physical symptoms like shaking, sweating, and tachycardia.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
Episodes of anxiety symptoms like panic attacks and insomnia, caused by an experience or a series of experiences of trauma. This pattern persists possibly for the rest of one’s life, even if the trauma is extinguished, never to return.
- Selective mutism
Being unable to speak in certain situations due to anxiety, such as a child who cannot speak during school but has a normal speaking ability at home.
- Separation anxiety disorder
When separation from a caregiver or loved one causes anxiety that interferes with the ability to function and it is not normal as it is in babies or young children.
- Situational anxiety
The anxiety of abnormal frequency, length, or strength invoked by a new situation that makes a person uncomfortable.
- Social anxiety disorder
Abnormal anxiety in social situations. People with a social anxiety disorder may experience isolation and depression as well.
- Specific phobias
Specific phobias are excessive fears attached to specific objects like bats, spiders, or bridges that significantly affect the quality of life.
Conventional Anxiety Treatment
The usual treatment for anxiety is either medication or psychotherapy. Each has been shown to be effective in some cases.
Psychotherapeutic treatment may involve Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, a talk therapy aimed at providing social comfort to the client, and challenging negative thought patterns. Therapy or life coaching can also be delivered online.
Medication Treatment for anxiety may involve several categories of medication. The first line is antihistamines like hydroxyzine (Vistaril, Atarax). Next is benzodiazepines like Valium and Klonopin. The use of such medications has been restricted due to tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal. Antidepressants like Paxil are also used in the treatment of anxiety disorders.
What is CBD?
CBD stands for cannabidiol. It is the decarboxylated form of CBD-A or cannabidiol carboxylic acid. When heated, this acid becomes CBD. CBDA occurs naturally in Cannabis Sativa, Cannabis Indica, and Cannabis Ruderalis (hemp with low THC). CBD is the second most abundant cannabinoid in a pot, second only to THC.
What is CBD Oil?
CBD oil is made by using a solvent to extract CBD and evaporating to concentrate the CBD which will be suspended in the hemp oil. CBD oil can be taken orally or applied topically. CBD oil is not something most people will want to smoke.
CBD may also be suspended in other oils like milk butter, coconut oil, and olive oil.
The legality of CBD oil
Thirty states have laws legalizing and protecting CBD and marijuana for restricted medical use. Another Seventeen allow the use of low or no-THC CBD preparations. Epidiolex, a prescription CBD product, is federally recognized as a Schedule V medication. CBD itself, however, is still federally a controlled Schedule I substance. Lawmakers have made promises to legalize CBD federally, but this has yet to go through. CBD oil can be obtained in most states with minimal risk of prosecution. See what the marijuana laws are in your state at our site here: https://leaf.expert/english/business-law/medical-marijuana-card
CBD oil disclaimers (please read, this is important):
General Medical Disclaimer
Leaf Expert and its employees and partners do not represent the medical establishment and our information is not a replacement for your doctor’s advice.
FDA Disclaimer
The use of CBD products with the exception of Epidiolex and Sativex has not been evaluated or approved by the FDA.
Drug Screening Disclaimer
While most CBD products claim to have little to no THC, it is theoretically possible to fail a drug test for THC. This can happen because some CBD products have been tested to have far more THC than represented on the label. Also, CBD is similar in structure to THC.
“Feel free to discuss any unclear points, our community will help you”
Does CBD have any side effects?
CBD tends to have few side effects, therefore, we include this section last. None-the-less, prescription CBD labels such as from Epidiolex and Sativex include the following possible side effects:
- infection
- little appetite
- rash
- sleep disturbance
- suicidal thoughts
- diarrhea
- drowsiness
- elevated liver enzymes
- fatigue
Conclusion:
Looking at the evidence of safety and benefits, we theorize that CBD should be the first-line therapy for anxiety disorders. It appears even to have fewer side effects than antihistamines like Vistaril and Benadryl. We give an A, pending further studies and anecdotal reports.
Bibliography
Bergamaschi, M. M., Queiroz, R. H., Chagas, M. H., Oliveira, D. C., Martinis, B. S., Kapczinski, F., . . . Crippa, J. A. (2011). Cannabidiol Reduces the Anxiety Induced by Simulated Public Speaking in Treatment-Naïve Social Phobia Patients. Neuropsychopharmacology, 36(6), 1219-1226. Retrieved 10 28, 2018, from https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21307846
Bonn-Miller, M. O., Loflin, M., Thomas, B. F., Marcu, J. P., Hyke, T., & Vandrey, R. (2017). Labeling the Accuracy of Cannabidiol Extracts Sold Online. JAMA, 318(17), 1708-1709. Retrieved 10 27, 2018, from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2661569
Fusar-Poli, P., Fusar-Poli, P., Allen, P., Bhattacharyya, S., Crippa, J. A., Crippa, J. A., . . . McGuire, P. (2010). Modulation of effective connectivity during emotional processing by Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 13(4), 421-432. Retrieved 10 28, 2018, from https://academic.oup.com/ijnp/article/13/4/421/712253
Hundal, H., Lister, R., Evans, N., Antley, A., Englund, A., Murray, R. M., . . . Morrison, P. D. (2018). The effects of cannabidiol on persecutory ideation and anxiety in a high trait paranoid group. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 32(3), 276-282. Retrieved 10 28, 2018, from http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0269881117737400
Jurkus, R., Day, H. L., Guimarães, F. S., Lee, J. L., Bertoglio, L. J., & Stevenson, C. W. (2016). Cannabidiol Regulation of Learned Fear: Implications for Treating Anxiety-Related Disorders. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 7, 454. Retrieved 10 28, 2018, from https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc5121237
Lee, J. L., Bertoglio, L. J., Guimarães, F. S., & Stevenson, C. W. (2017). Cannabidiol regulation of emotion and emotional memory processing: relevance for treating anxiety-related and substance abuse disorders. British Journal of Pharmacology, 174(19), 3242-3256. Retrieved 10 28, 2018, from https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28268256
Zuardi, A. W., Shirakawa, I., Finkelfarb, E., & Karniol, I. G. (1982). The action of cannabidiol on the anxiety and other effects produced by δ9-THC in normal subjects. Psychopharmacology, 76(3), 245-250. Retrieved 10 28, 2018, from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/bf00432554
- 1 How much CBD oil to take for anxiety?
- 2 Our choice: Sublingual
- 3 How to Choose a CBD Oil for Anxiety
- 4 How does CBD oil work for Anxiety?
- 5 Pros and cons CBD VS Conventional Treatment for Anxiety
- 6 Research on CBD for Anxiety
- 7 Reviews: Wisdom of Social Media
- 8 About Anxiety
- 9 Conventional Anxiety Treatment
- 10 What is CBD Oil?
- 11 CBD oil disclaimers (please read, this is important):
- 12 Does CBD have any side effects?
- 13 Conclusion:






